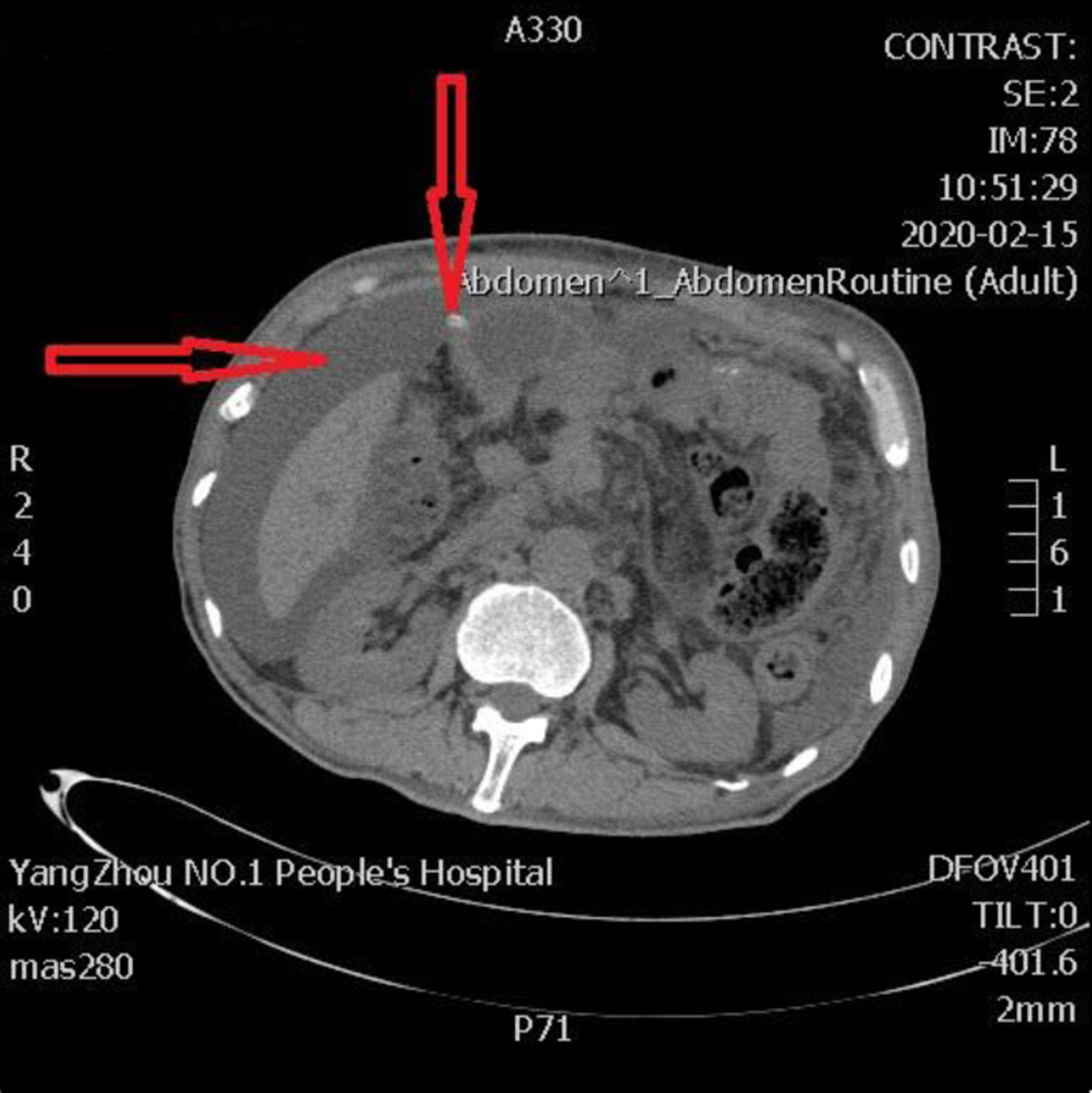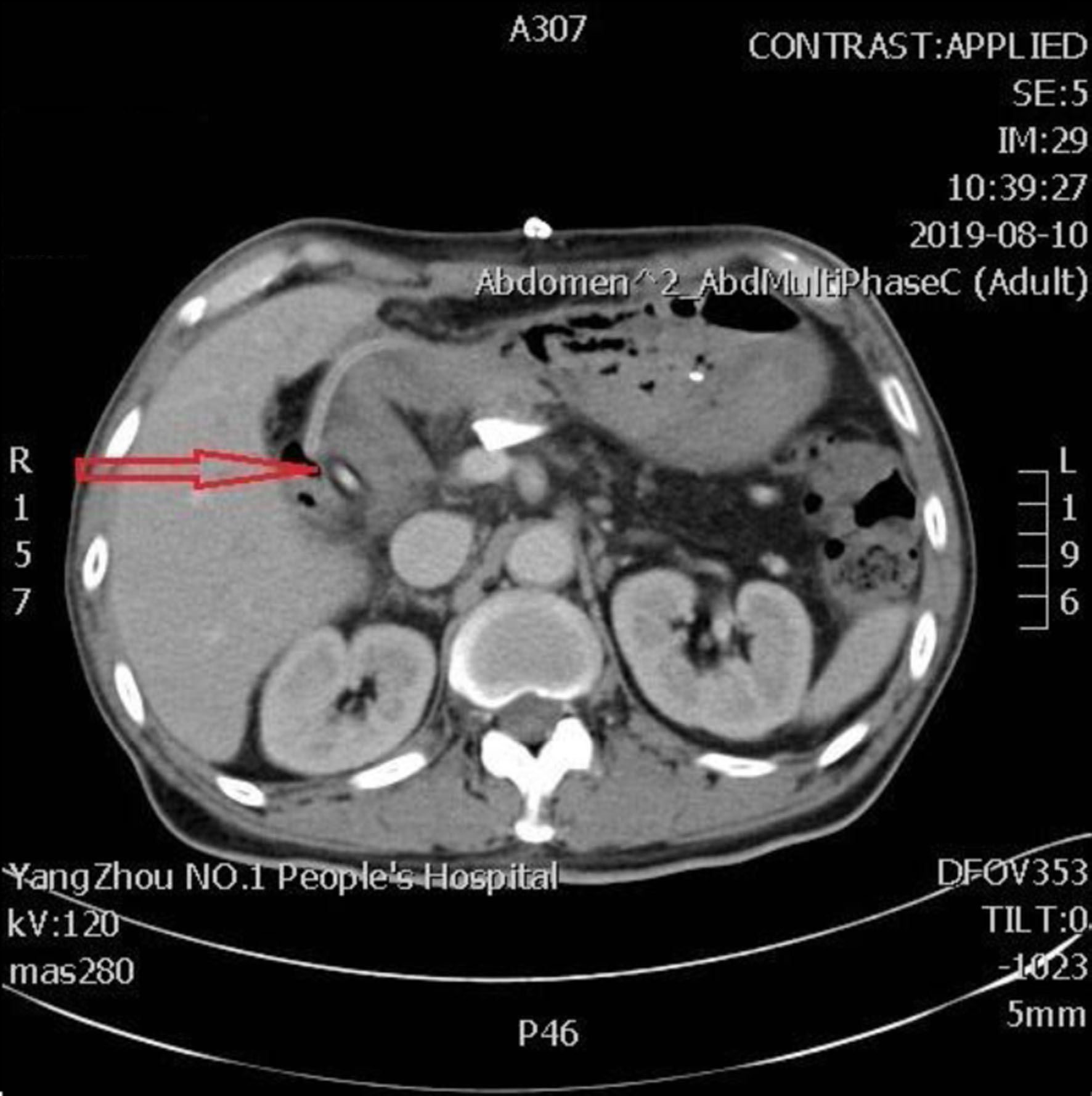
Figure 1. The second day after PD, the abdominal CT scan shows the pancreatic intraductal stent in place, extending from the main pancreatic duct into the intestinal lumen (arrow). CT: computed tomography; PD: pancreaticoduodenectomy.
| Journal of Current Surgery, ISSN 1927-1298 print, 1927-1301 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Curr Surg and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jcs.elmerpub.com |
Case Report
Volume 15, Number 1, March 2025, pages 26-28
Post-Pancreaticoduodenectomy Jejunal Perforation and Pancreatic Fistula Caused by Pancreatic Intraductal Stent
Figures